JavaScript 中的 Trie:什么是前缀树?
前言
我们已经在三篇文章中介绍了树数据结构的基础知识。如果你还没有读过这些,我强烈建议先阅读前三篇文章:
介绍
Trie 是树数据结构的一种变体。它也被称为前缀树或搜索树的变体。就像 n 叉树数据结构一样,trie 可以有 n 个来自单亲的孩子。通常,trie 中的所有节点都会存储一些字符。假设我们只处理英语单词,下面是一个简单的 trie 可能看起来像:
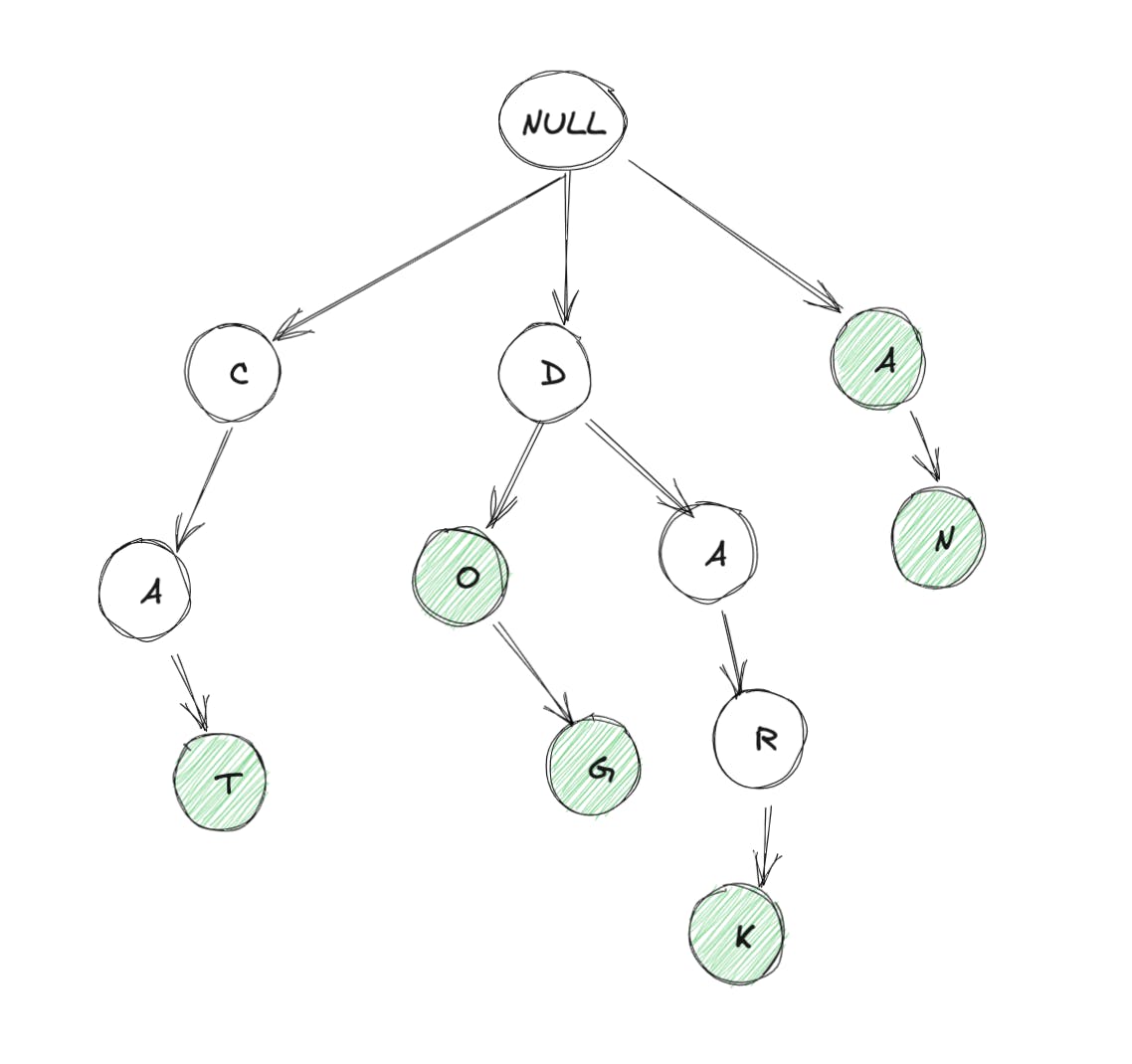
需要注意的事项:
-
我们正在尝试使用树来尽可能高效地表示英语单词。
-
在上图中,从根节点到任何绿色节点的路径表示一个英文单词。例如:
- NULL->C->A->T: CAT
- NULL->D->O: DO
- NULL->D->O->G: DOG
- NULL->D->A->R->K: DARK
- NULL->A: A
- NULL->A->N: AN
-
每个节点最多可以有 26 个子节点(如果我们只处理英文字母)。我们有一个 NULL 节点作为根节点,因为一个单词可以以 26 个字母中的任何一个开头,因此我们需要一个虚拟节点,它可以将任何潜在的第一个字母作为子节点。
-
绿色节点,本质上代表“词尾”,同时从根遍历到该节点。
实现节点
现在,让我们尝试提出 Trie 节点的表示。回到树节点,这就是我们呈现它的方式:
function Node(value){
this.value = value
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
因此,我们可以对 Trie 遵循类似的想法,同时确保它满足我们在介绍部分讨论的要求。要了解 Trie 节点的要求,让我们放大任何节点:
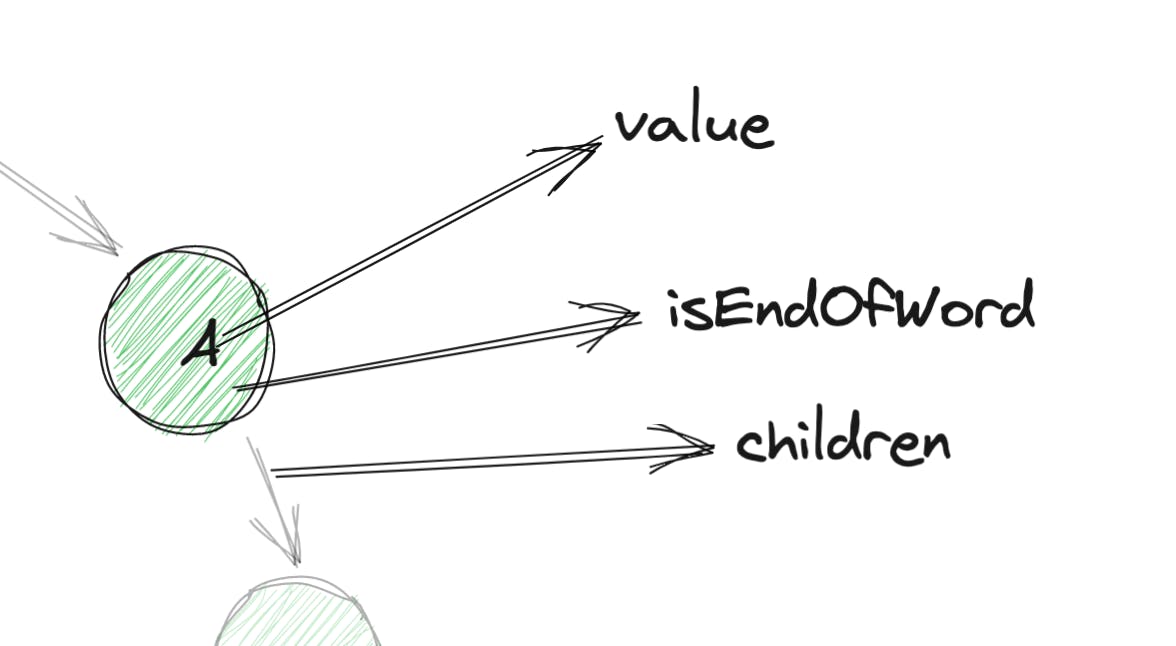
所以现在更有意义了。这是最终的代码:
function Node(value){
this.value = value
this.isEndOfWord = false // false by default, a green node means this flag is true
this.children = {} // children are stored as Map, where key is the letter and value is a TrieNode for that letter
}
实现 Trie 数据结构
我们可以使用一个简单的 ES6 类来表示:
class Trie{
constructor(){
this.root = new Node(null)
}
insert(word){
// TODO
}
search(word){
// TODO
}
}
所以我们已经准备好了大概。作为初始化的一部分,每个trie 都会创建它自己的根节点(NULL)。那么我们可以实现这两个方法如下:
- insert(word):我们可以将单词拆分为字母,并为每个字母创建一个 Node()。然后我们可以开始将这些 Trie 节点中的每一个链接到根节点,以插入单词。最后,我们将最后插入的节点的 isEndOfWord 属性标记为 true。
- search(word):我们可以将单词拆分为字母。然后我们可以从根开始一个一个地寻找这些字母中的每一个。如果我们能够按顺序找到所有字母,那么我们可以返回 true 否则 false。
让我们直观地理解这两个操作以获得更好的上下文:
- 首先insert(CAR)然后insert(CAN):
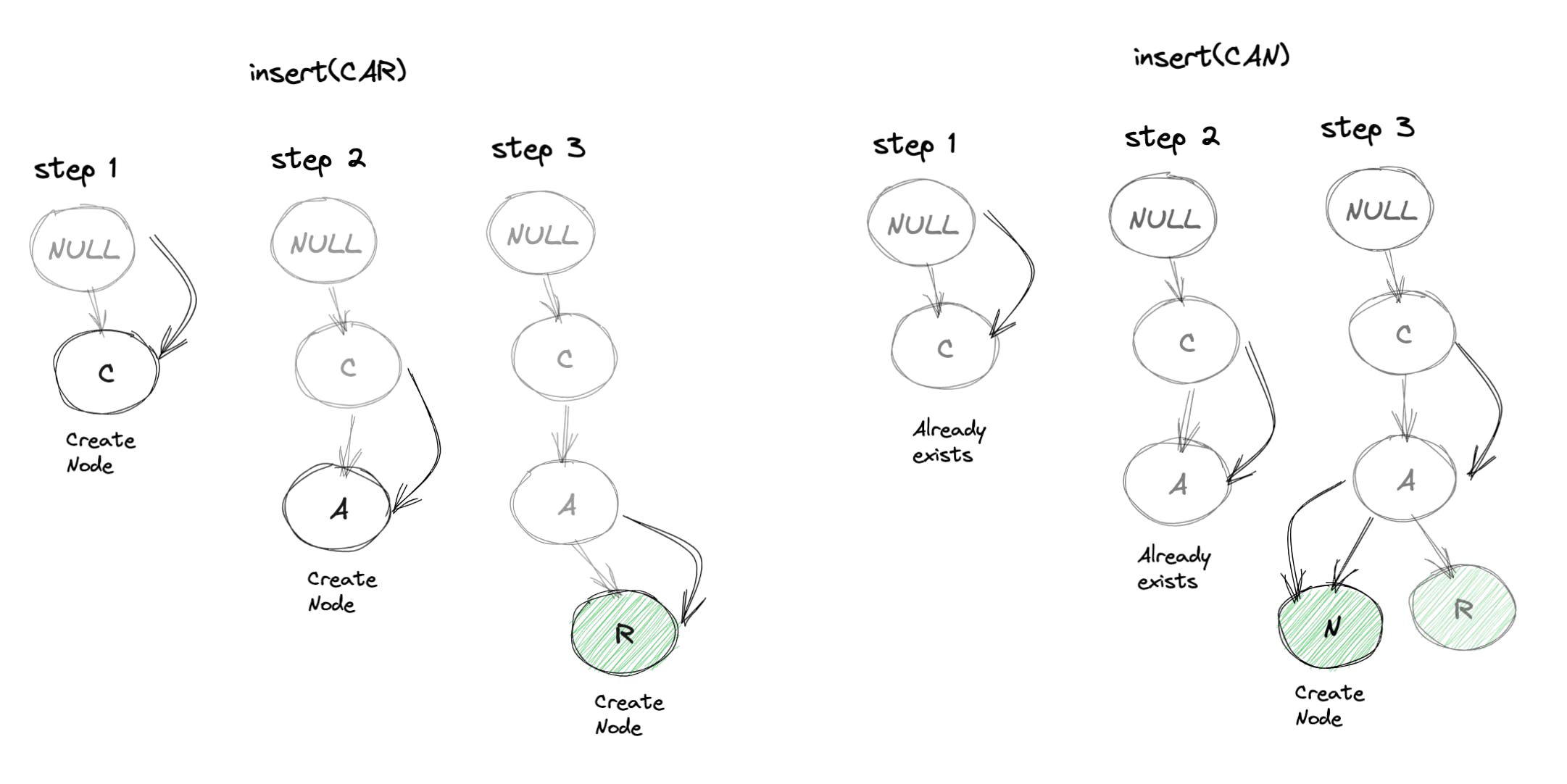
- 首先search(CAR)然后search(CAN):
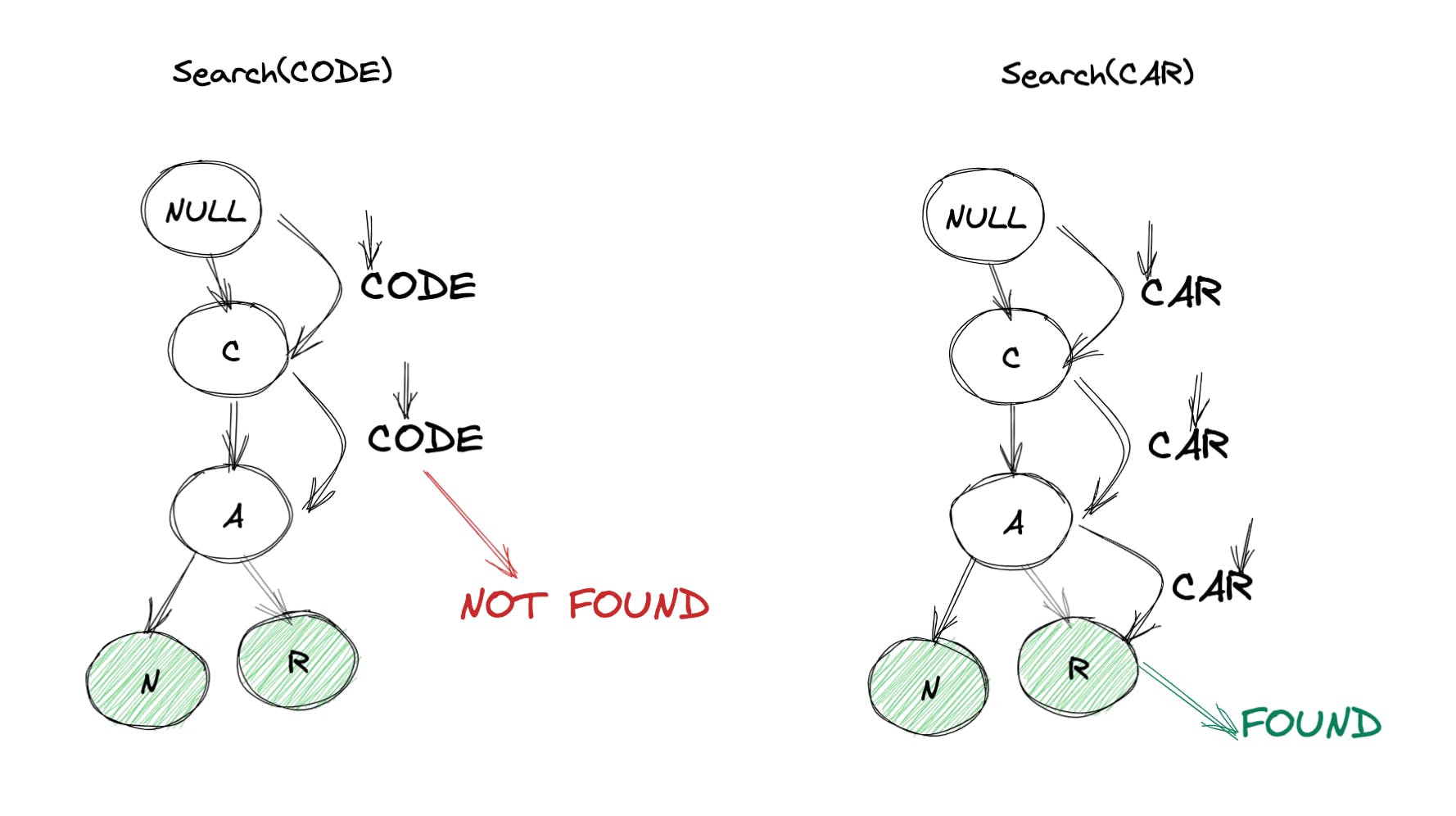
实现如下:
class Trie{
constructor(){
this.root = new Node(null)
}
insert(word){
let current = this.root
// iterate through all the characters of word
for(let character of word){
// if node doesn't have the current character as child, insert it
if(current.children[character] === undefined){
current.children[character] = new Node(character)
}
// move down, to insert next character
current = current.children[character]
}
// mark the last inserted character as end of the word
current.isEndOfWord = true
}
search(word){
let current = this.root
// iterate through all the characters of word
for(let character of word){
if(current.children[character] === undefined){
// could not find this character in sequence, return false
return false
}
// move down, to match next character
current = current.children[character]
}
// found all characters, return true if last character is end of a word
return current.isEndOfWord
}
}
使用 Trie
const trie = new Trie();
// insert few words
trie.insert("CAT");
trie.insert("DOG");
// search something
trie.search("MAT") // false
trie.search("DOG") // true
空间复杂度
在最坏的情况下,所有插入单词的每个字符都可以占用 Trie 中的单个节点。所以这意味着最坏的空间复杂度可以是 (W*n),其中 W 是每个单词的平均字符数,n 是 Trie 中的单词总数。
时间复杂度
- 插入:插入一个有n个字符的单词,只需要遍历n个字符,所以时间复杂度为O(n)
- 搜索:与插入类似,我们只需要遍历单词的所有字符即可进行搜索。所以时间复杂度是 O(n),其中 n 是单词中的字符数。
现在,想一想,你还能如何在庞大的单词列表中搜索某个单词?
-可能使用数组?时间复杂度为 O(m),其中 m 是单词总数,这很糟糕。
- 如何使用Map(或 JavaScript 中的对象)?这会将时间复杂度降低到 O(1),但是找到具有特定前缀的单词列表有多快?它将是 O(m)。
Trie 不仅将时间复杂度降低到 O(n)(n = 单词中的字符数),而且您还可以有效地搜索具有前缀的单词列表,这对于任何以上两种方法。
应用
- 自动完成和预先输入:如果您在文本框中键入内容,并且看到具有相同前缀的潜在搜索列表,即自动完成小部件,那么这可能是由后台的 Trie 处理的。同样,Typeahead 也可以使用 Trie 来实现。
- 拼写检查器:我们可以使用 trie 创建拼写检查器,即给定一个单词列表,我们可以检查给定单词的拼写是否正确。
- IP 路由(最长前缀匹配):Internet 由多个路由器节点组成,它们决定应该发送的目标数据包。 Internet 上的每个路由器都需要将数据包发送到由给定 IP 目的地决定的适当目标节点。但是每个路由器如何使用给定的 IP 地址决定下一个目标路由器呢?这个问题可以使用IP路由来解决。这是一篇深入探讨这个主题的好文章。