JavaScript 中的 Tree
前言
Tree是一种有趣的数据结构。它在各个领域都有广泛的应用。例如:
- DOM 是一种Tree状数据结构
- 我们操作系统中的目录和文件可以表示为Tree
- 家庭层次结构可以表示为Tree。
Tree的许多变体(如堆、BST 等)可用于解决与调度、图像处理、数据库等相关的问题。许多复杂的问题乍一看似乎与Tree无关,但可以被表示为一个Tree的问题。我们也会(在本系列的后面部分)解决这些问题,从而了解Tree如何使看似复杂的问题更容易理解和解决。
简介
二叉树实现节点非常简单
function Node(value){
this.value = value
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
// usage
const root = new Node(2)
root.left = new Node(1)
root.right = new Node(3)
所以这几行代码将为我们创建一个二叉树,如下所示:
2
/ \
/ \
1 3
/ \ / \
null null null null
遍历
让我们从尝试遍历这些连接的树节点(或一棵树)开始。正如我们可以遍历数组一样,如果我们也可以“遍历”树节点。然而,树不是像数组那样的线性数据结构,所以遍历这些的方法不止一种。我们可以将遍历方法大致分为以下几类:
- 广度优先遍历
- 深度优先遍历
广度优先遍历(BFS)
在这种方法中,我们逐层遍历树。我们将从根开始,然后覆盖它的所有子级,然后覆盖所有 2 级子级,依此类推。例如对于上面的树,遍历会导致这样的结果:
2
/ \
/ \
1 3
/ \ / \
null null null null
2,1,3
下面是一个稍微复杂的树的插图,使这更容易理解:
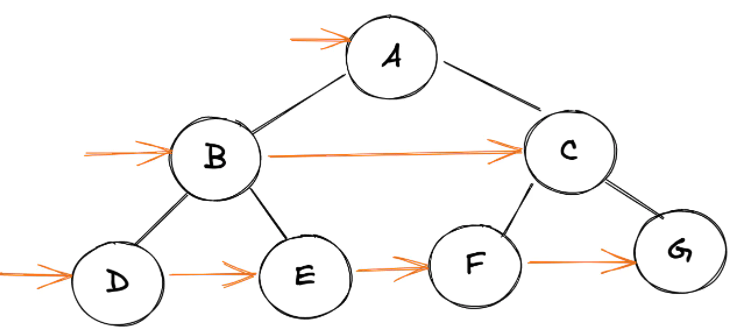
为了实现这种形式的遍历,我们可以使用队列(先进先出)数据结构。以下是整个算法的过程:
- 初始化一个包含 root 的队列
- 从队列中删除第一项
- 将弹出项的左右节点推入队列
- 重复步骤 2 和 3,直到队列为空
下面是这个算法在实现后的样子:
function walkBFS(root){
if(root === null) return
const queue = [root]
while(queue.length){
const item = queue.shift()
// do something
console.log(item)
if(item.left) queue.push(item.left)
if(item.right) queue.push(item.right)
}
}
我们可以稍微修改上面的算法实现为:
function walkBFS(root){
if(root === null) return
const queue = [root], ans = []
while(queue.length){
const len = queue.length, level = []
for(let i = 0; i < len; i++){
const item = queue.shift()
level.push(item)
if(item.left) queue.push(item.left)
if(item.right) queue.push(item.right)
}
ans.push(level)
}
return ans
}
深度优先遍历(DFS)
在 DFS 中,我们取一个节点并继续探索它的子节点,直到深度耗尽为止。它可以通过以下方式之一完成:
root node -> left node -> right node // pre-order traversal
left node -> root node -> right node // in-order traversal
left node -> right node -> root node // post-order traversal
所有这些遍历技术都可以递归和迭代实现。让我们进入实现细节:
前序遍历(Pre-Order traversal)
分析
root node -> left node -> right node
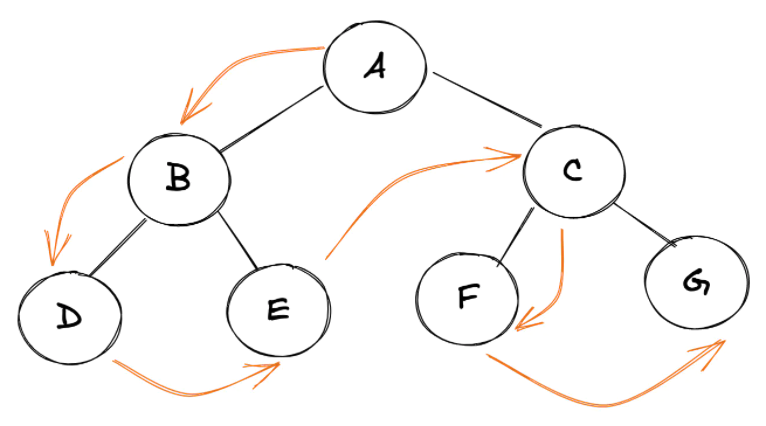
技巧:
我们可以使用这个简单的技巧来手动找出任何树的前序遍历:从根节点开始遍历整棵树,保持自己在左边。
实现
- 递归
function walkPreOrder(root){
if(root === null) return
// do something here
console.log(root.val)
// recurse through child nodes
if(root.left) walkPreOrder(root.left)
if(root.right) walkPreOrder(root.right)
}
- 迭代
前序遍历的迭代方法与 BFS 非常相似,不同之处在于我们使用堆栈而不是队列,并且我们首先将右节点推入堆栈:
function walkPreOrder(root){
if(root === null) return
const stack = [root]
while(stack.length){
const item = stack.pop()
// do something
console.log(item)
// Left child is pushed after right one, since we want to print left child first hence it must be above right child in the stack
if(item.right) stack.push(item.right)
if(item.left) stack.push(item.left)
}
}
中序遍历(In-Order traversal)
分析
下面是一棵树的中序遍历的过程:
left node -> root node -> right node
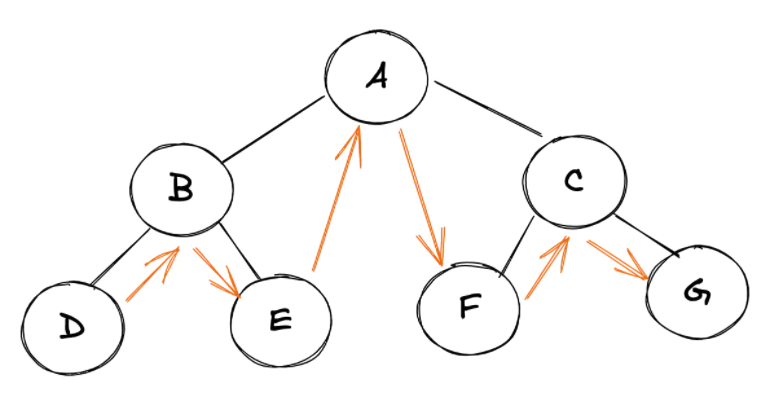
技巧
我们可以使用这个简单的技巧来手动找出任何树的中序遍历:在树的底部水平放置一个平面镜,并获取所有节点的投影
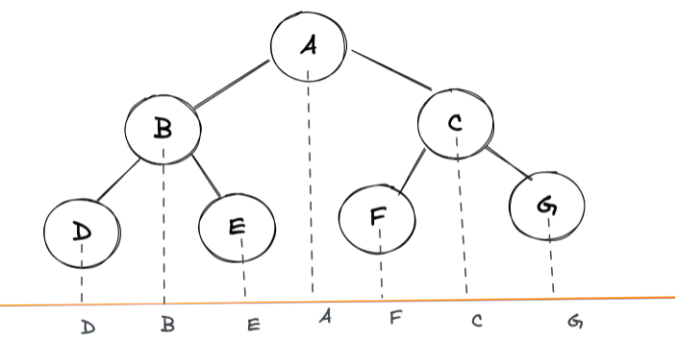
实现
- 递归
function walkInOrder(root){ if(root === null) return if(root.left) walkInOrder(root.left)
// do something here
console.log(root.val)
if(root.right) walkInOrder(root.right)
}
- 迭代
这个算法乍一看可能有点神秘。但它相当直观。让我们这样看:在中序遍历中,最左边的孩子节点首先被打印,然后是根,然后是孩子节点。所以首先想到的是想出这样的东西:
```javascript
const curr = root
while(curr){
while(curr.left){
curr = curr.left // get to leftmost child
}
console.log(curr) // print it
curr = curr.right // now move to right child
}
在上述方法中,我们无法回溯,即返回导致最左侧节点的父节点。所以我们需要一个堆栈来记录这些。因此,我们修订后的方法可能如下所示:
const stack = []
const curr = root
while(stack.length || curr){
while(curr){
stack.push(curr) // keep recording the trail, to backtrack
curr = curr.left // get to leftmost child
}
const leftMost = stack.pop()
console.log(leftMost) // print it
curr = leftMost.right // now move to right child
}
现在我们可以使用上面的方法来制定最终的迭代算法:
function walkInOrder(root){
if(root === null) return
const stack = []
let current = root
while(stack.length || current){
while(current){
stack.push(current)
current = current.left
}
const last = stack.pop()
// do something
console.log(last)
current = last.right
}
}
后序遍历(Post-Order traversal)
分析
下面是一棵树的中序遍历的过程:
left node -> right node -> root node
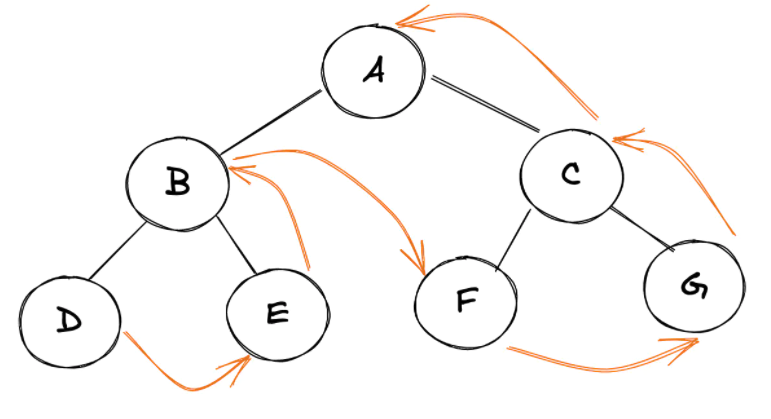
技巧
对于任何树的快速手动后序遍历:一个接一个地提取所有最左边的孩子节点。
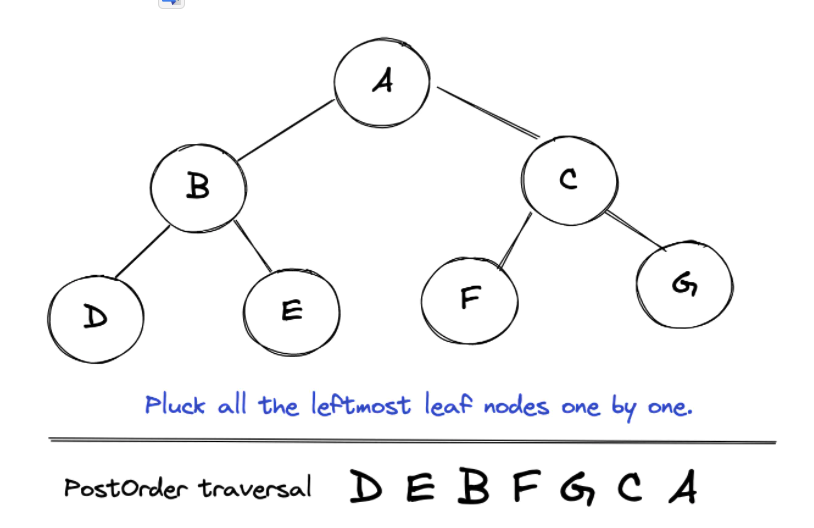
实现
让我们深入研究这种遍历的实际实现。
- 递归
function walkPostOrder(root){ if(root === null) return if(root.left) walkPostOrder(root.left) if(root.right) walkPostOrder(root.right) // do something here console.log(root.val) } - 迭代
我们已经有了用于前序遍历的迭代算法。我们可以用那个吗?因为后序遍历似乎只是前序遍历的反向。让我们来看看:
// PreOrder:
root -> left -> right
// Reverse of PreOrder:
right -> left -> root
// But PostOrder is:
left -> right -> root
从上面分析可见有细微的差别。我们可以通过稍微修改我们的 前序遍历算法然后反转它应该给出 后序遍历结果来适应这一点。总体算法将是:
// record result using
root -> right -> left
// reverse result
left -> right -> root
- 使用与上述迭代前序遍历算法类似的方法,使用临时堆栈。
- 唯一的区别是 root -> right -> left 而不是 root -> left -> right
- 结果将遍历序列记录在一个array
- 结果的反转就是后序遍历
function walkPostOrder(root){
if(root === null) return []
const tempStack = [root], result = []
while(tempStack.length){
const last = tempStack.pop()
result.push(last)
if(last.left) tempStack.push(last.left)
if(last.right) tempStack.push(last.right)
}
return result.reverse()
}